In a photovoltaic (PV) system, the electricity generated is primarily used to power loads. When the generation exceeds the load demand, excess electricity flows back into the grid, creating a "reverse current." Grid regulations typically restrict unpermitted backflow, and unauthorized power feeding can result in penalties. For PV projects designed for self-consumption without grid feeding, anti-backflow protection is crucial for achieving sustainable energy independence.
What Is Anti-Backflow?
In a PV system, the solar modules produce direct current (DC), which is converted to alternating current (AC) by an inverter to supply local loads. If the generation exceeds the consumption, the surplus electricity flows back into the grid, creating backflow. Systems with anti-backflow functionality can adjust the inverter's output to ensure that the electricity generated is fully consumed by local loads, preventing excess power from entering the grid.
Why Install Anti-Backflow?
The main reasons for installing anti-backflow include:
1. Grid Policy Restrictions: In some regions, grid constraints or policies prohibit feeding power into the grid. Unauthorized backflow may lead to penalties.
2. Grid Connection Limitations: The grid imposes strict limits on the amount of power that can be fed into it. Exceeding these limits without control can disrupt grid stability.
3. Self-Consumption Principle: PV systems designed for self-use prioritize local load consumption. Any excess power must be blocked from entering the grid using anti-backflow devices.
Working Principle of Anti-Backflow
Anti-backflow systems typically involve an anti-backflow meter and current transformer (CT) installed on the mainline. These components measure real-time power and current flow. When reverse current is detected, the meter communicates the backflow data to the inverter via RS485 communication. The inverter responds within seconds, reducing its output power to ensure the current flow into the grid is nearly zero.
Anti-Backflow Solutions
Different configurations are available to meet various scenarios:
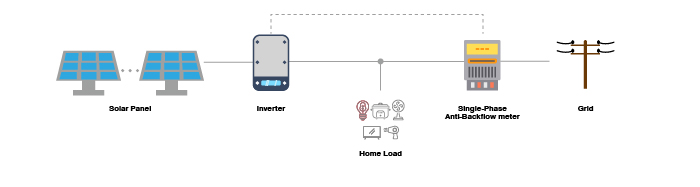
1. Single-Phase Anti-Backflow System Solution
· Required equipment: grid-tied inverter, anti-backflow meter, and communication cable.
· Suitable for small-scale residential PV systems.
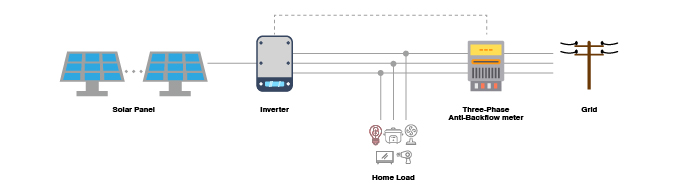
2. Three-Phase Anti-Backflow System Solution
· For low-power residential systems, DC anti-backflow meters can be directly connected to the inverter's AC output terminals.
· For high-power systems, CT transformers detect the current on the grid connection point. The CT output is scaled and fed into the anti-backflow meter for precise power measurement.
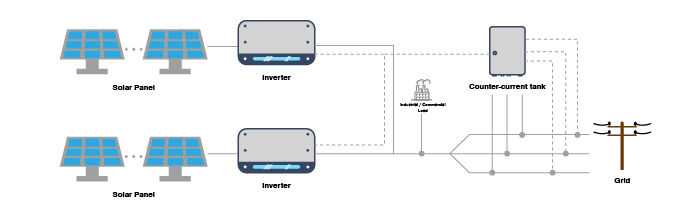
3. Multi-Inverter Anti-Backflow System Solution
· Multiple inverters are connected via communication interfaces to a data logger.
· This solution is ideal for large-scale setups, offering higher capacity and more robust functionality.
Summary
Anti-backflow solutions address the "grid-connected but non-feed-in" policy requirements of specific regions. They enhance grid stability, improve system safety, optimize energy efficiency, and adapt to evolving technologies and policies. By employing tailored anti-backflow systems, PV projects can ensure compliance, reliability, and economic viability.







